Home / E-Invoicing Requirements in the EU, Switzerland, and the UK: A High-Level Overview
E-Invoicing Requirements in the EU, Switzerland, and the UK: A High-Level Overview
- Last updated: June 4, 2023
- Invoice management
Product Manager
Gone are the days of sending traditional paper invoices through the mail; e-invoicing leverages digital systems to seamlessly transmit invoice data from one platform to another.
But what is e-invoicing and why should you care about it?
While it finds particular relevance in B2B transactions, e-invoicing holds the potential to benefit businesses of all sizes, ranging from small enterprises to large corporations, across various industries such as services and product-based companies.
So let’s dive into the topic and see what e-invoicing is and how you can prepare your tech stack for adopting such solutions.
What is e-invoicing and how does it work?
E-invoicing, also known as electronic invoicing, is a method of creating, sending, receiving, and processing invoices electronically.
The e-invoicing process involves two parties: the supplier who issues the invoices, and the receiver – either a customer, in B2C transactions, or another company, in business-to-business transactions. The supplier creates and issues the invoice, while the client receives it.
E-invoicing rules affect several aspects of invoice processing:
- the invoice format – what an invoice must look like
- the creation of invoices – how invoices should be issued
- the sending of invoices – what channel or platform companies should use
- the receipt and processing of invoices – how invoices should be handled
Let’s break this down a little further.
Format and structure
EU e-invoicing rules specify the format that invoices must adhere to. In most cases, invoices need to be in a standardized structured data format that allows for automatic reading of the data into computer systems, to facilitate automated processing.
Common formats include XML (Universal Extensible Markup Language), EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), or other standardized formats such as UBL (Universal Business Language) or JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). These formats ensure consistency and enable systems to process invoices electronically.
However, it’s essential to review specific country regulations as there might be slight variations in the required formats.
The creation of invoices and compliance with tax regulations
Businesses need to ensure that the invoice creation process follows the prescribed format and includes all the necessary information required by the relevant authorities.
In its simplest form, an electronic invoice must contain all the required details of a paper invoice. The following information must be included:
- Unique identification number for each invoice, commonly known as the invoice number.
- Issue date of the invoice.
- Time of supply which refers to the date when the work was performed and/or payment was received.
- Supplier’s name and address.
- Customer’s name and address.
- Supplier’s VAT (Value Added Tax) number.
- Description of the goods or services provided.
- Price of the goods or services, preferably specified in countable units.
- Quantity or extent of the goods sold.
- VAT rate applicable to the goods or services.
- Amount owed or paid, excluding VAT.
- Total amount of VAT charged.
- Any discounts applied to the invoice.
In some countries, e-invoices may need to meet specific tax compliance standards, such as those outlined by the European Union’s Directive on e-invoicing.
Authentication and integrity
To ensure the authenticity and integrity of e-invoices, various mechanisms are often employed. Digital signatures or electronic certificates can be used to authenticate the sender and verify that the invoice hasn’t been tampered with during transmission.
Data exchange and interoperability
E-invoices should be easily exchanged and processed between different systems and organizations. For example, the EU regulation stipulates that e-invoices must be sent and received through a designated system, and this is a mandatory requirement.
Interoperability standards, such as PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement On-Line), facilitate seamless transmission and processing of e-invoices across different entities and systems.
Storage and archiving
E-invoices are typically required to be stored and archived for a certain period of time to comply with legal and auditing requirements. The storage methods may vary, but they often involve electronic archiving systems that ensure the integrity, accessibility, and long-term preservation of the invoices.
It’s important to note that specific regulations and requirements for e-invoicing may differ from country to country. Therefore, it is advisable to consult local tax authorities or seek professional advice to ensure compliance with applicable regulations in your jurisdiction.
Check out our newsletter
Don't miss out
Join 12’000+ finance professionals and get the latest insights on spend management and the transformation of finance directly in your inbox.
How is e-invoicing different from digital and traditional invoicing?
Electronic invoicing is not just the digitization of invoices, meaning that e-invoicing is not the same with digital invoicing. Electronic invoicing requires companies to adhere to specific requirements set by different jurisdictions, and impacts the end-to-end process.
So although digital invoices and e-invoices both refer to invoices in an electronic format, the compliance with the various regulations is the key aspect here and is what differentiates e-invoicing from invoice digitalization.
Who must comply with e-invoicing regulations?
The implementation of e-invoicing regulations impacts every business that sends or receives invoices from clients or suppliers, making e-invoicing a necessity for businesses operating in the EU.
However, there are additional parties who should comply with e-invoicing regulations. Here are some examples:
- Suppliers and vendors: They are responsible for providing e-invoices that meet the required standards and formats.
- Customers and clients: They may need to ensure their systems and processes can handle e-invoices and integrate them into their accounting or payment systems.
- IT service providers and software vendors: They need to develop or provide e-invoicing solutions that meet the regulatory standards and requirements.
- Financial institutions: They may need to ensure their systems can handle e-invoices and facilitate secure and efficient payment transactions.
- Government agencies and regulatory bodies: They should comply with the regulations themselves and oversee compliance in the business sector.
These parties are involved in the e-invoicing ecosystem and should comply with the regulations to ensure smooth and standardized electronic invoicing processes.
To provide detailed insights into the rules and requirements, let’s explore the specific regulations and important dates for e-invoicing in selected countries within the EU, such as the Netherlands, Germany, Austria, Spain, France, Italy, Switzerland, and the UK.
E-invoicing regulations within EU, UK, and Switzerland
The European Union has already adopted e-invoicing as a standard practice. The Directive 2014/55/EU requires all public authorities to be able to receive and process electronic invoices in a standardized format (such as XML), the due date being April 2019.
The European Commission has also established the European E-invoicing Service Providers Association (EESPA) to promote the adoption of e-invoicing and ensure interoperability between different e-invoicing systems.
Still, note that e-invoicing regulations and compliance requirements vary by country and region. Here is an overview of some of the major regulations and compliance requirements.
Netherlands e-invoicing regulations
In the Netherlands, e-invoicing is encouraged but not mandatory for businesses. However, the government has implemented the PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement Online) network, which enables electronic invoicing between businesses and government entities.
To summarize:
Invoice format: E-invoices in the Netherlands should comply with the European e-invoicing standard and be structured in specific formats, such as UBL or XML. Businesses are responsible for creating e-invoices in the prescribed formats, ensuring accurate and complete invoice data.
Sending of invoices: E-invoices can be sent through various channels, including EDI, email, or via the PEPPOL network, which facilitates secure and standardized transmission. More information on PEPPOL here.
Source: E-invoicing Netherlands
Germany e-invoicing regulations
Germany has implemented e-invoicing regulations in compliance with the European Directive on e-invoicing. Public sector entities in Germany are required to accept electronic invoices in a standardized format, such as XRechnung or ZUGFeRD. Private companies are also encouraged to adopt e-invoicing to improve efficiency.
As of May 2023, Germany has not enforced mandatory e-invoicing for non-government transactions. However, the country has formulated plans to introduce e-invoicing regulations, aiming for implementation by 1 January 2025.
To summarize:
Invoice format: In Germany, e-invoices must comply with specific formats like XRechnung, Factur-X, or ZUGFeRD. ZUGFeRD is a cross-industry hybrid format that offers a unique advantage to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It provides invoices in two formats: an image representation (PDF-A/3) and a machine-readable E-Invoice data record in XML format.
Sending of invoices: In Germany, e-invoices should be submitted through the central platform called “Zentraler Rechnungseingang des Bundes” (Central Invoice Receipt of the Federal Government) or ZRE.
Compliance in Germany
Stay up-to-date with rules and regulations around per diem rates – including the midnight rule and 3-month rule, mileage allowances, proof of receipt, and VAT rates in Germany, while Yokoy keeps you audit-ready.
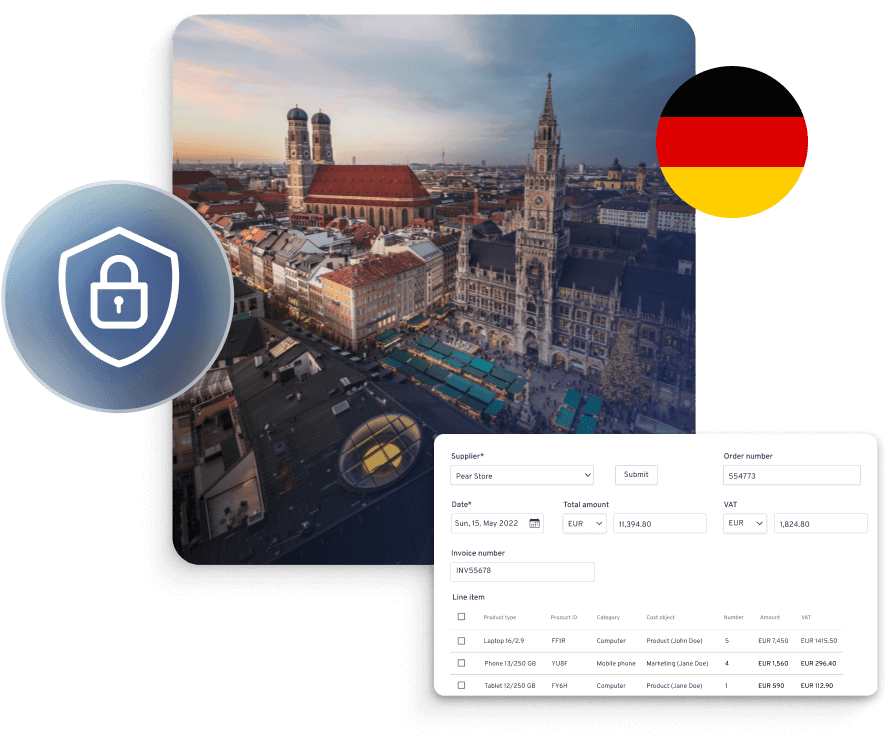
Austria e-invoicing regulations
In Austria, e-invoicing regulations focus primarily on business-to-government (B2G) transactions. The Austrian government has implemented mandatory e-invoicing for suppliers who provide goods and services to public entities.
The requirement for e-invoicing in Austria is based on the European Directive on e-invoicing (2014/55/EU) and is aimed at promoting standardized and digital invoicing practices.
To summarize:
- Invoice format: In Austria, e-invoices must follow the European e-invoicing standard and be structured in a specific format. Two formats, ebInterface (Austrian XML Standard) and Peppol UBL (Universal Business Language) are accepted for e-invoice submission in Austria.
- E-invoices can be submitted through the E-RECHNUNG.GV.AT platform. Suppliers can also choose to utilize other approved channels or e-invoicing platforms that comply with the technical requirements set by the Austrian government.
- Sending and receiving invoices: The recommended channel for sending e-invoices in Austria is through the PEPPOL network, which ensures secure and standardized transmission.
Compliance in Austria
Stay up-to-date with rules and regulations around per diem rates, mileage allowances, proof of receipt, and VAT rates in Austria, while Yokoy keeps you audit-ready.

Spain e-invoicing regulations
In Spain, the use of e-invoicing is mandatory for both public and private sector transactions. The Spanish Tax Agency (AEAT) requires businesses to submit electronic invoices in a specific XML format, Facturae. This regulation aims to enhance tax control, streamline processes, and combat tax fraud.
To summarize:
Invoice format: E-invoices in Spain must be created and stored in an approved XML format, following specific technical requirements set by the Spanish tax authority, AEAT.
Sending of invoices: E-invoices can be sent through various channels, including EDI, email, or using certified e-invoicing platforms that comply with Spanish regulations.
Compliance in Spain
Stay up-to-date with rules and regulations around per diem rates, mileage allowances, proof of receipt, and VAT rates in Spain, while Yokoy keeps you audit-ready.

France e-invoicing regulations
In France, e-invoicing regulations apply to both business-to-government (B2G) and business-to-business (B2B) transactions. For B2G transactions, e-invoicing is mandatory for suppliers invoicing French public entities.
The French tax authority, Direction Générale des Finances Publiques (DGFiP), provides guidelines and technical specifications for e-invoicing compliance.
To summarize:
- Invoice format: E-invoices can be generated in structured XML files or PDFs with embedded data. Businesses are responsible for creating e-invoices according to the specified technical requirements, ensuring accurate and complete information.
- Sending of invoices: E-invoices in France can be sent through various channels, including electronic data interchange (EDI), email, or via the Chorus Pro platform, which is the designated e-invoicing platform for public procurement.
E-invoicing regulations in Italy
Italy has implemented a mandatory e-invoicing system known as “FatturaPA” since 2019. This system requires businesses to issue and transmit electronic invoices in a standardized format through the government-controlled platform called the Sistema di Interscambio (SDI).
To summarize:
Invoice format: In Italy, e-invoices must be issued in the XML format based on the Italian FatturaPA standard. This format ensures compliance with the legal requirements and enables interoperability between different systems.
Creation of invoices: E-invoices must include mandatory information such as the issuer’s and recipient’s details, invoice date, invoice number, description of goods/services, quantity, unit price, total amount, applicable taxes (including VAT), and other relevant invoice data.
Sending of invoices: The SDI acts as a central hub for sending and receiving invoices securely. E-invoices undergo validation checks by the SDI to ensure compliance with the required format and data accuracy. In case of any errors or discrepancies, proper correction procedures need to be followed.
E-invoicing regulations in Switzerland
Since 2016, business-to-government (B2G) electronic invoicing has been mandatory in Switzerland. E-invoicing for B2B and B2C in Switzerland is not currently mandatory but is widely adopted, and all invoices are subject to the 10-year archiving period.
The Swiss government supports the use of structured e-invoice formats as a means to improve efficiency and reduce costs, and promotes interoperability among different e-invoicing platforms.
Many Swiss companies voluntarily adopt e-invoicing practices to streamline their invoicing processes.
To summarize:
- Invoice format: E-invoices in Switzerland are not subject to specific prescribed formats but are encouraged to be structured and compatible with standardized e-invoicing practices. Businesses have flexibility in creating e-invoices according to their internal processes, as long as they comply with interoperability standards and best practices.
- Sending of invoices: E-invoices can be sent through various channels, including EDI, email, or using e-invoicing platforms that support interoperability.
Compliance in Switzerland
Stay up-to-date with rules and regulations around per diem rates, mileage allowances, proof of receipt, and VAT rates in Switzerland, while Yokoy keeps you audit-ready.

E-invoicing regulations in the UK
The UK has introduced e-invoicing requirements for suppliers dealing with the UK public sector. Suppliers must use the government’s PEPPOL-compliant network, known as the NHS Shared Business Services (SBS), to send electronic invoices to public sector organizations.
To summarize:
Invoice format: E-invoices in the UK do not have specific prescribed formats, but businesses are encouraged to adopt structured formats such as XML or other industry-standard formats.
Creation of invoices: Businesses have flexibility in creating e-invoices, ensuring they contain all the required information for accurate invoicing and compliance purposes.
Sending of invoices: E-invoices can be sent through various channels, including EDI, email, or using e-invoicing platforms that support secure transmission.
What are the benefits of e-invoicing?
To list just some of the benefits of electronic invoicing solutions:
Time and cost savings: E-invoicing eliminates the need for manual invoice creation, printing, and mailing, reducing administrative tasks and associated costs.
Faster payment cycles: E-invoicing enables the rapid delivery and receipt of invoices, allowing businesses to streamline payment cycles and improve cash flow management.
Reduced risk of errors: E-invoicing minimizes human errors by automating data capture and validation processes.
Improved supplier and customer relationships: Efficient and accurate invoicing processes contribute to smoother payment experiences, enhancing trust between business partners.
Financial transparency and reporting: E-invoicing provides better visibility into financial transactions, as electronic invoices can be easily tracked, monitored, and integrated with accounting and ERP systems, enabling real-time financial reporting and analysis.
Streamlined operations: E-invoicing can seamlessly integrate with other business systems such as accounting software, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and procurement platforms. This integration streamlines the end-to-end invoicing process, automating tasks like invoice matching, approval workflows, and payment reconciliation.
Environmental sustainability: E-invoicing eliminates the need for invoice printing and physical mailing, demonstrating a commitment to environmental responsibility.
These benefits explain the widespread adoption of e-invoicing, which reflects a global shift towards digital transformation and process optimization in general. Electronic invoicing is becoming a standard practice, which means that now it’s the right time to adopt such solutions.
Next steps
To sum it up, preparing your tech stack to adopt e-invoicing solutions is a crucial step towards unlocking a range of benefits for your business.
By seamlessly integrating electronic invoicing into your existing systems, you can experience significant advantages that will enhance your overall operations and drive growth.
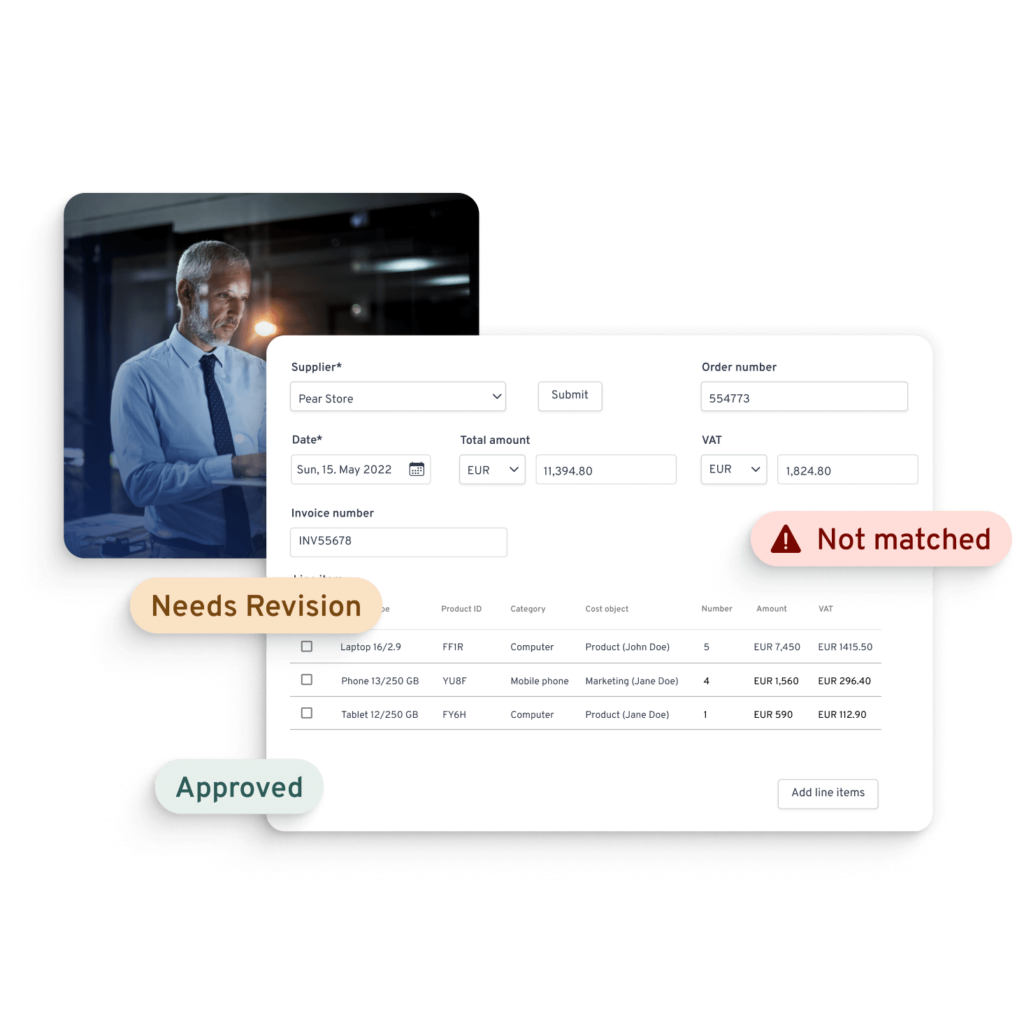
Through our partnerships, Yokoy offers full e-invoicing support, streamlining and automating the invoice management process. This reduces your overall operating costs, improves spend visibility and enables you to better balance your spend and budgets to inform investments.
Through AI automation, Yokoy invoice reduces errors to a minimum, ensuring faster invoice processing and approval times, and lower processing costs. At the same time, it helps enforce policy compliance and reduce fraud.
To see our invoice management solution in action, book a demo below.
Yokoy Invoice
Process invoices automatically
Streamline your accounts payable process to manage invoices at scale and pay suppliers on time with Yokoy’s AI-powered invoice management solution.
Simplify your spend management
Related content
If you enjoyed this article, you might find the resources below useful.